Accutane is the number one teratogen on the market. A teratogen is a medication that interferes with normal development of the fetus and causes birth defects. Shortly after Accutane became available on the market, the Centers for Disease Control reported that a large proportion of pregnancies in women who are exposed to Accutane result in spontaneous abortions and birth defects and advised against the use of Accutane by pregnant women. You should never take Accutane (isotretinoin) or any of the generic versions of Accutane if you are pregnant or trying to get pregnant or could accidentally become pregnant.
Accutane unwanted effects
If a patient has any of the following symptoms of an allergic reaction such as difficulty breathing, hives or swelling of the throat, lips, face or tongue, stop using the medicine and seek emergency medical help immediately.
If the patient is experiencing any of the following side effects, he or she should stop taking the medication and consult a healthcare professional:
- Joint stiffness, bone fracture or pain
- Red skin rash or severe blistering and peeling
- Easy bruising or bleeding, purple spots under the skin, flu symptoms, body aches, chills, fever
- Jaundice, clay-colored stools, dark urine, loss of appetite
- Fast heart rate, vomiting and nausea, severe pain starting in the upper stomach spreading to the back
- Convulsions or seizures
- Ringing in the ears, hearing loss or other hearing problems
- Blurred vision, severe pain or headache behind the eyes, with or without vomiting
- Sudden weakness or numbness, particularly on one side of the body
- Thoughts of hurting yourself or suicide, hallucinations, changes in behavior, agitation or aggression, crying spells, insomnia or sleep problems, difficulty concentrating, depression
Less severe side effects of Accutane include:
- Changes in toenails or fingernails, rash, itching, peeling or cracking skin
- Dryness of the skin, nose, mouth or lips
- Feeling nervous, drowsy or dizzy
- Back and joint pain
- Fatigue
- Muscle aches
- Bleeding or swollen gums
- Increased sensitivity to UV rays
- Voice changes
- Headache
- Cold Symptoms
- Increased bone injuries resulting from weakened or thickened bones
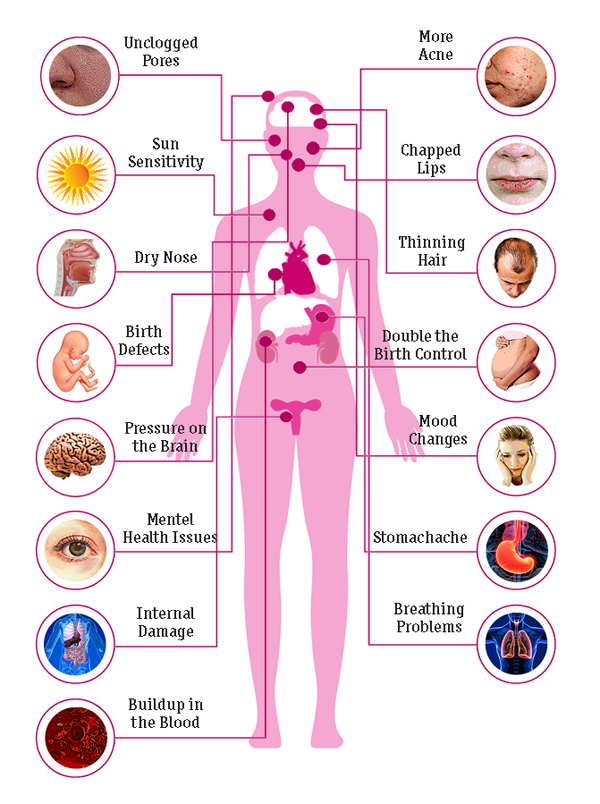
The more serious side effects of isotretinoin can have long-term or permanent effects. However, apart from increased cholesterol and joint and muscle problems, these side effects are all quite rare.
Increased cholesterolIsotretinoin can increase the levels of fats and cholesterol in your blood. During your treatment, your doctor may suggest regular blood tests to check your fat and cholesterol levels. You're at higher risk of these problems if you:
- have diabetes
- are obese
- have metabolic syndrome
- drink alcohol
This side effect, if you have it, typically goes away when you finish your treatment with isotretinoin.
Joint and muscle problemsTell your doctor if you plan to do hard physical activity during treatment with isotretinoin. Isotretinoin can cause pain in your bones, joints, muscles, and ligaments. It can also stunt the growth of long bones in teens, which could have permanent effects. If you have any of the following symptoms, call your doctor right away:
- new back pain
- new joint pain
- broken bone
If you break a bone, be sure to tell all of the healthcare providers that care for you that you take isotretinoin.
If you have muscle weakness, with or without pain, stop taking isotretinoin and call your doctor right away. Muscle weakness can be a sign of serious muscle damage and could be a permanent effect.
Pressure on your brainRarely, isotretinoin can cause increased pressure on the brain. This can lead to permanent loss of eyesight and, in rare cases, death. Stop taking isotretinoin and call your doctor right away if you have any of these symptoms:
- severe headache
- blurry vision
- dizziness
- nausea and vomiting
If you have either of these symptoms, call 911 right away:
- seizures
- stroke
Although rare, a rash caused by isotretinoin can be serious. Stop using isotretinoin and call your doctor right away if you have any of the following symptoms:
- conjunctivitis (pink eye)
- a rash with fever
- blisters on your arms, legs, or face
- peeling skin
- sores in your mouth, throat, nose, or eyes (on the lid or the eye itself)
Isotretinoin can damage your internal organs. These organs include your liver, pancreas, intestines, and esophagus (the tube connecting your mouth and stomach). The damage may not get better even after you stop taking isotretinoin.
This side effect is rare. Still, stop taking isotretinoin and call your doctor right away if you have any of the following symptoms:
- severe pain in your stomach, chest, or lower abdomen
- trouble swallowing or pain during swallowing
- new or worsening heartburn
- diarrhea
- bleeding from your rectum
- yellowing of your skin or the whites of your eyes
- dark urine
Isotretinoin can cause serious hearing problems in rare cases. Stop using isotretinoin and call your doctor right away if your hearing gets worse or if you have ringing in your ears. Any hearing loss may be permanent.
Vision and eye problemsIsotretinoin can cause vision problems such as blurry vision, double vision, and tunnel vision. This drug can also reduce your ability to see in the dark. Vision problems may fix themselves after you stop taking the drug or the damage may be permanent.
Isotretinoin can cause your eyes to produce more tears than normal. If you wear contact lenses, you may have trouble wearing them while taking isotretinoin. Like the other vision problems, this problem may go away after your stop treatment or it may be permanent.
All of these vision and eye problems are rare. Nevertheless, stop taking isotretinoin and call your doctor right away if you have problems with your vision, an increased amount of tears, or painful or constant eye dryness.
Allergic reactionsIsotretinoin can cause serious allergic reactions in rare cases. Stop taking isotretinoin and call your doctor if you have a rash, red patches, or bruises on your legs or a fever. If you have any of the following symptoms, stop taking isotretinoin and call 911 or go to the nearest emergency room:
- hives
- swelling in your face or mouth
- trouble breathing
Isotretinoin may cause blood sugar problems, including diabetes. Call your doctor if you have any of the following symptoms:
- severe thirst
- urinating more often
- blurry vision
- increased tiredness
These may be diabetic symptoms caused by the drug. This effect is rare, though.
Low red blood cell levelsAnother rare, serious side effect is a decrease in blood cell levels. Low levels of red blood cells can cause problems such as anemia. Call your doctor if you have any of the following symptoms:
- extreme tiredness
- weakness
- dizziness
- coldness in your hands and feet
- pale skin
Low levels of white blood cells raise your risk of infections. Call your doctor if you have any of the following symptoms:
- fever
- frequent infections
This side effect is rare.
Mental health issuesRarely, isotretinoin can cause serious mental health problems. These include depression, psychosis (losing touch with reality), and suicidal thoughts or actions. Stop using isotretinoin and call your doctor right away if you have any of the following symptoms:
- increased feelings of sadness
- crying spells
- loss of interest in activities you enjoy
- sleeping too much or trouble sleeping
- acting more irritable, angry, or aggressive than usual
- changes in appetite or weight
- lack of energy
- withdrawal from friends or family
- trouble concentrating
- feelings of worthlessness or guilt
- thoughts of hurting yourself or taking your own life
- hallucinations (seeing or hearing things that are not real)
How to take Accutane
It is recommend that the individual take this medication with a full glass of water; if the pill cannot be swallowed fully, it may become lodged in the esophagus and melt, causing irritation. Individuals are advised not to suck or chew on the capsule and to swallow as quickly as possible. Some may also consider taking Accutane with milk or food. Always take the medicine for the full length of time as prescribed by a doctor.
Those taking Accutane should do so exactly as directed by a healthcare professionals. Avoid taking the medicine in smaller or larger amounts or for a longer period of time than recommended. When a patient receives a prescription for Accutane, he or she must fill it within one week; a prescription is for a 30-day supply only. The recommended dosage for the medication is 0.5 to 1.0 mg/kg per day typically taken in two divided doses. Food is often suggested with the medication to avoid the risk of an upset stomach and to help absorption. Before physicians will increase the dosage of the medicine, they may verify that the patient has been taking the medication with food. However, during treatment, a physician may adjust the dose depending on the response of the acne or the appearance of side effects. Additionally, some adult patients with a severe disease may benefit from 2.0 mg/kg per day as tolerated. If the total number of acne lesions has been reduced by over 70 percent before completing 16 to 20 weeks of treatment, the physician may recommend that the drug be discontinued. Long-term use of the drug has not been fully evaluated, even in low doses, and is typically not recommended.

